Will Texas have to push back the expiration dates on its lethal injection drugs?
/https://static.texastribune.org/media/images/Lethal-Injection_Split.jpg)
*Clarification appended.
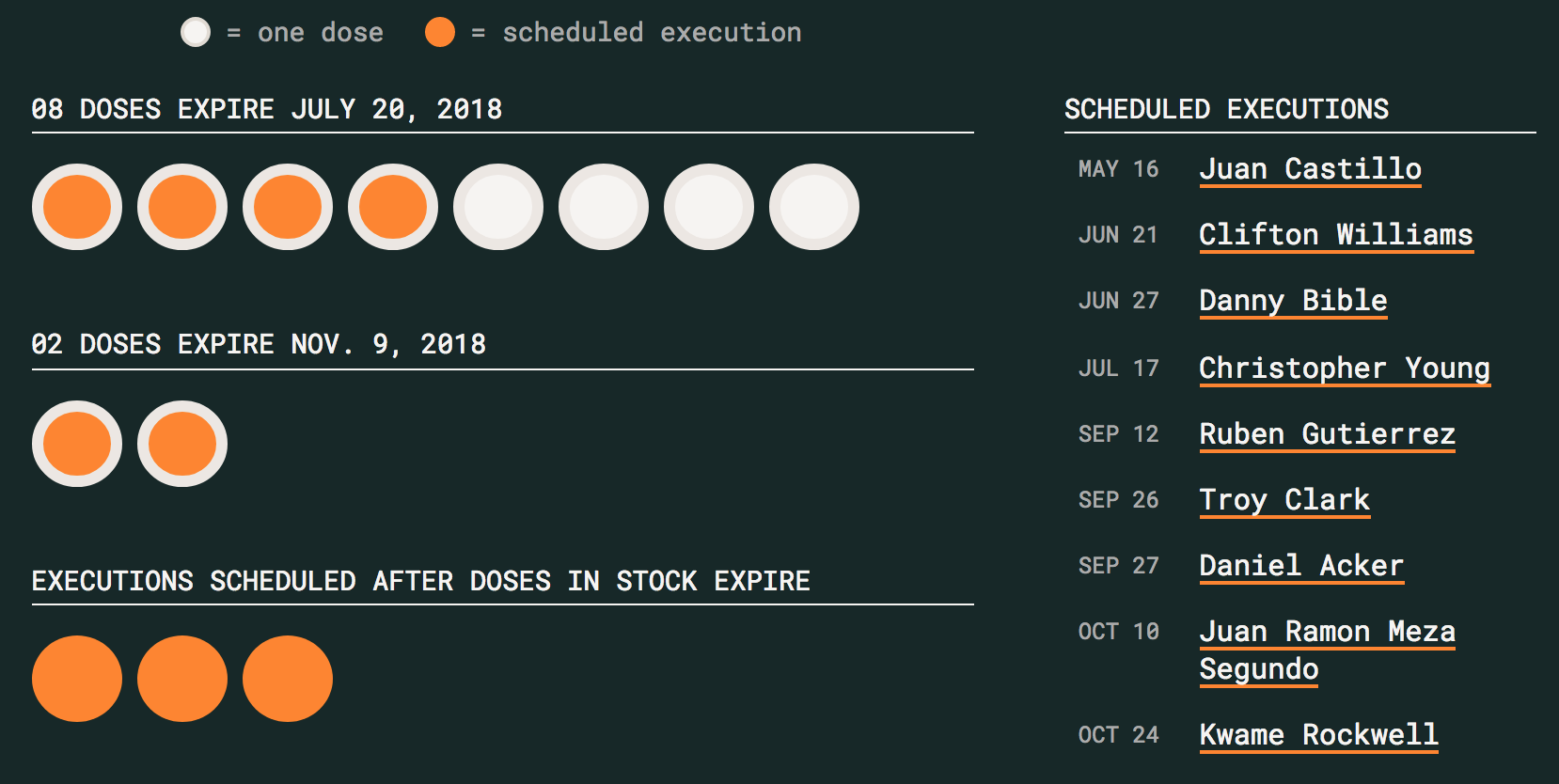
Soon after Texas officials put Juan Castillo to death Wednesday night, a prison spokesman said the department was in possession of enough lethal injection drugs to carry out the remaining six executions scheduled for this year.
Minutes later, the spokesman, Jeremy Desel, announced two more pending executions for the fall. But records obtained by The Texas Tribune on Monday indicated that the state’s supply of drugs was insufficient. Unless the state were to push back the expiration dates of its current supply or track down more of the hard-to-find drugs, at least three of the condemned men would be set to die after available drugs expire.
Desel refused to say on Thursday if "beyond-use dates," similar to expiration dates, were changed on the current supply or if new drugs were purchased, telling a Tribune reporter that a new records request would need to be filed for any updated information. But he repeatedly said that the department was "confident that we are adequately prepared for all scheduled executions."
According to records provided to the Tribune on Monday, the department had 10 doses of pentobarbital, the single drug used in Texas executions. Eight of those doses had a beyond-use date of July 20, and the other two were labeled for use until Nov. 9.
At least one of those was used in Castillo’s death, meaning there are likely now nine doses available. Recent executions have used the drugs set to expire in November, but the department did not immediately say Thursday morning which batch of drugs was used in Castillo’s execution.
Regardless, only three of the eight upcoming executions are scheduled before July 20. Even if the state switched tactics from recent executions and used the batch with a use date of July on Castillo, the November drugs would only cover two of the five executions set in September and October.
Across the country, death penalty states have struggled to get enough drugs to carry out executions. In 2011, large manufacturers began blocking their drugs from being used in lethal injections, and several states have since switched to using a controversial drug, midazolam, which has been involved in botched executions in Oklahoma and Arizona.
When Texas struggled to find execution drugs years ago, it turned to compounding pharmacies, which are state-regulated agencies that mix their own drugs without federal regulation. Since 2013, it has only used pentobarbital created in these types of pharmacies in its executions.
But that supply might be running dry as well. Recent records obtained by the Tribune showed the state hadn’t received a new batch of drugs since February 2017, and the state recently battled with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration over its attempted import of another execution drug, sodium thiopental, from India.
The current beyond-use dates, however, don’t necessarily mean the state won’t carry out the executions. Both batches of pentobarbital the state has now have seemingly had their beyond-use date extended in the past.
According to TDCJ records received by the Tribune last year, drugs set to expire in July 2017 were removed from stock, and, on the same day, the same number of vials were added back to the inventory with an expiration date set for exactly one year in the future. Those are now set to be used before this July. And an equal number of drugs said to expire in January were later reported with the current beyond-use date of November, with no recorded purchase of additional drugs. The expiration dates were apparently changed after the department retested the drugs’ potency levels, records show.
The apparent extension of expiration dates produced outcry from some defense attorneys, one of whom said in a recent death penalty appeal that recent Texas executions were botched because of the old drugs, causing pain and making the punishment cruel and unusual.
“The thinking is they’re only getting older; it’s only going to get worse,” Maurie Levin told the Tribune earlier this year. Levin is involved in multiple lawsuits against the state regarding execution drugs.
“I'd bet good money that they will simply be extending the [beyond-use date] of the drugs that expire in July,” she added Thursday afternoon.
Multiple men in Texas executions this year have mentioned a burning sensation when on the gurney in the death chamber, according to reporters witnessing the execution. The Houston Chronicle reported in January that Houston serial killer Anthony Shore said, “It does burn.” In Castillo’s execution Wednesday, he reportedly said, “Shit does burn.” Another man, William Rayford, reportedly jerked on the gurney, according to witnesses.
A previous spokesman for the department denied that Shore or Rayford’s executions were botched, saying the men quickly lost consciousness and were both pronounced dead 13 minutes after lethal drugs were injected. Castillo’s execution took 23 minutes.
Clarification: This story has been updated to more clearly reflect the timing of Jeremy Desel's comments.
Information about the authors
Learn about The Texas Tribune’s policies, including our partnership with The Trust Project to increase transparency in news.
/https://static.texastribune.org/media/profiles/04_Jolie_McCullough_MG.jpg)